Understanding Pips, Lots, and Spreads in Forex Trading
Introduction
If you’re new to forex trading, you’ll often hear terms like pips, lots, and spreads. These are fundamental concepts that every trader must understand, as they directly affect your profits, losses, and overall trading performance.
This guide will explain what pips, lots, and spreads are, how they’re calculated, and why they matter in real trading scenarios.
What is a Pip?
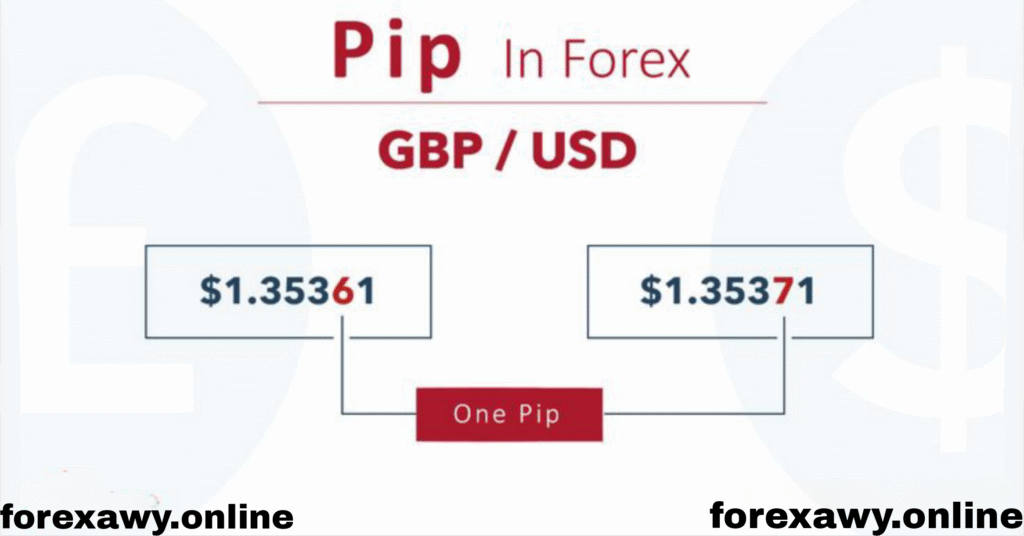
Pip stands for “Percentage in Point” or “Price Interest Point”. It is the standard unit of measurement for price movements in the forex market.
In most currency pairs, a pip equals 0.0001.
For example, if EUR/USD moves from 1.1050 to 1.1051, that’s a movement of 1 pip.
Exception:
For pairs involving the Japanese Yen (like USD/JPY), a pip equals 0.01.
Why Pips Matter
Pips are used to:
- Measure the change in currency prices
- Calculate profit and loss
- Determine spreads (cost of trading)
What is a Lot?
In forex, a lot refers to the size or volume of a trade. It tells you how many units of the base currency you’re buying or selling.
There are several standard lot sizes:
| Lot Type | Units |
|---|---|
| Standard Lot | 100,000 units |
| Mini Lot | 10,000 units |
| Micro Lot | 1,000 units |
| Nano Lot | 100 units |
When you place a trade, the number of lots determines how much each pip movement is worth.
Example:
- 1 Standard Lot (EUR/USD): 1 pip = $10
- 1 Mini Lot: 1 pip = $1
- 1 Micro Lot: 1 pip = $0.10
How to Calculate the Value of a Pip
The pip value depends on:
- The currency pair being traded
- The lot size
- The exchange rate
For a USD-based pair (like EUR/USD), pip value is easy to calculate.
Formula:
Pip Value = (One Pip / Exchange Rate) × Lot Size
Example:
- You trade 1 Standard Lot of EUR/USD at 1.1200
- One pip = 0.0001
- Pip Value = (0.0001 / 1.1200) × 100,000 ≈ $8.93
Most platforms do this calculation automatically, but it’s useful to understand the math.
What is a Spread?
The spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair.
- Bid price: The price at which the broker will buy the base currency from you.
- Ask price: The price at which the broker will sell the base currency to you.
Spread = Ask Price – Bid Price
Example:
If EUR/USD is quoted as:
- Bid: 1.1048
- Ask: 1.1050
Then the spread = 1.1050 – 1.1048 = 2 pips
Why Spreads Matter
Spreads are a cost of trading. When you open a position, you start with a small loss equal to the spread.
- Tight spreads = lower trading cost
- Wide spreads = higher trading cost
Spreads vary by:
- Currency pair (major pairs usually have lower spreads)
- Market volatility
- Broker type (ECN vs. market maker)
Fixed vs. Variable Spreads
- Fixed Spread: The spread remains constant, regardless of market conditions. Common with market maker brokers.
- Variable Spread: Changes depending on market volatility and liquidity. Common with ECN brokers.
Combining the Concepts
Let’s look at a real-world example:
- You open a 1 Mini Lot trade on EUR/USD
- Entry price: 1.1000
- Exit price: 1.1010
- Movement: 10 pips
- Pip value: $1 (because 1 Mini Lot)
Profit = 10 pips × $1 = $10
But if the spread was 2 pips, your net profit would be:
- 10 pips – 2 pips = 8 pips
- 8 × $1 = $8
Always factor in the spread before calculating potential gains.
The Role of Leverage and Lot Size
Lot size works hand-in-hand with leverage, which allows you to control larger positions with less capital. However, larger lots amplify both profits and losses.
Example:
- Trading 1 Standard Lot (1 pip ≈ $10)
- A 20-pip loss = $200 loss
Choosing the right lot size and risk per trade is a key part of risk management.
Summary
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Pip | Smallest price movement in a currency pair |
| Lot | Size or volume of your trade |
| Spread | Difference between bid and ask prices |
Understanding these core elements will help you:
- Calculate potential profits and losses
- Set more accurate stop-loss and take-profit levels
- Manage risk more effectively
Conclusion
Pips, lots, and spreads form the foundation of every forex trade. Mastering these basics is essential for planning trades, controlling risk, and understanding how much money is actually at stake.
Before risking real money, make sure to practice on a demo account where you can experiment with different lot sizes and understand how spreads affect your positions. As you become more familiar with these concepts, you’ll gain more confidence and precision in your trading journey.